- #1
mandy9008
- 127
- 1
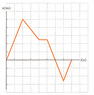
A graph of position versus time for a certain particle moving along the x-axis is shown in the figure below. Find the average velocity in the following time intervals. (The horizontal axis is marked in increments of 1 s and the vertical axis is marked in increments of 2 m.)
avg velocity = change in x / change in y
a. v= 2/10 = 0.2
b. v= 4/5 - 0.8
c. v= 2/0 = 0
d. v= 3/10 = 0.3
e. v= 8/5 = 1.6
avg velocity = change in x / change in y
a. v= 2/10 = 0.2
b. v= 4/5 - 0.8
c. v= 2/0 = 0
d. v= 3/10 = 0.3
e. v= 8/5 = 1.6