- #1
influx
- 164
- 2
I know what E-Z isomerism is, but I'm confused about Q9), couldn't the answer just be all of them?
FOr 10, I know its but- since there are 4 carbons in the chain but how do I know which of the options are wrong?
Thanks
sjb-2812 said:For 9 What do you understand by E / Z isomerism?
For 10 look into priorities for naming
sjb-2812 said:OK, does this compound show E / Z isomerism?
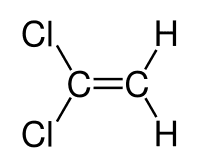
influx said:
The one on the left is B - it does show E-Z isomerism so B is the answer (right?).
Just out of curiosity, the one on the right is supposed to represent D, is it correct? Also how would I draw A and C?
Cheers
sjb-2812 said:Looks good to me :)
You'd draw A and C in a similar fashion, remembering that Carbon has a valence of 4 and Hydrogen 1. Each line represents a bond.
E-Z isomerism, also known as geometric isomerism, is a type of stereoisomerism in which molecules have different arrangements of atoms due to the presence of a double bond or ring. This results in different physical and chemical properties for each isomer.
Butane is a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C4H10. It is a straight-chain alkane with four carbon atoms connected by single bonds and ten hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms.
Butane can exist in two E-Z isomers, known as n-butane and isobutane. These isomers have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms around the double bond. N-butane has a linear structure, while isobutane has a branched structure.
The main difference between the E and Z isomers of butane is their physical properties. N-butane has a higher boiling point and is a liquid at room temperature, while isobutane has a lower boiling point and is a gas at room temperature. In terms of chemical properties, the two isomers may react differently due to their different arrangements of atoms.
E-Z isomerism is important in organic chemistry because it affects the reactivity and properties of molecules. It is also used to distinguish between different compounds with the same molecular formula. Understanding E-Z isomerism is crucial in fields such as drug development, where slight changes in molecular structure can greatly affect a compound's function and effectiveness.