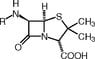
- #1
Adam_h
- 3
- 0
Hi, I have done quite a bit of looking about and I'm aware that there are many forms of penicillin...
While looking at the base structure of penicillin i have found two different kinds... At a guess i'd say one is synthetic and one is natural form?
Could someone possibly clear this up for me? Thanks in advance for any help you can provide.
Here are the two pictures of the chem structures, i need to know which is the main base for Pen...
Number 1 -
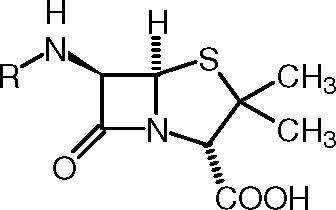
Number 2 -
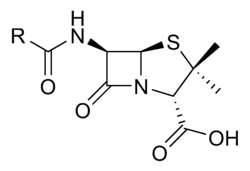
While looking at the base structure of penicillin i have found two different kinds... At a guess i'd say one is synthetic and one is natural form?
Could someone possibly clear this up for me? Thanks in advance for any help you can provide.
Here are the two pictures of the chem structures, i need to know which is the main base for Pen...
Number 1 -
Number 2 -