- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
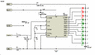
Can Some Help Explain This Circuit to me? its a LED Audio VU meter circuit
In summary, the circuit takes an audio input and compares it to a reference set. If the input is stronger, the LEDs will light up brighter.
Engineering news on Phys.org
- #2
schip666!
- 595
- 0
It would of course help to know the chip number or whatever...
But I'm not sure what needs explaining? It looks like it takes an audio input, through a "volume-control", compares it to a reference set with two resistors, and then (maybe?) lights up an array of LEDs based on the strength of the input.
Do you have some more specific questions?
But I'm not sure what needs explaining? It looks like it takes an audio input, through a "volume-control", compares it to a reference set with two resistors, and then (maybe?) lights up an array of LEDs based on the strength of the input.
Do you have some more specific questions?
- #3
uart
Science Advisor
- 2,795
- 21
The chip is an LM3915 and yep it's just a bunch of comparators set to switch in the LED's at different levels of the input signal. The circuit is pretty much the datasheet example for this IC. Not really much to explain.
- #4
AlephZero
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 6,982
- 298
That's what "LM3915" on the circuit diagram means.schip666! said:It would of course help to know the chip number or whatever...

The circuit is straight from the datasheet http://pdf1.alldatasheet.com/datasheet-pdf/view/8899/NSC/LM3915.html
What specifically don't you understand?
- #5
SammHunka
- 3
- 0
Basically i just need help understanding what the reference dc voltage connected to the top LED is for, what the variable resistor is for, and basically how the overall circuit works (meaning how the output is created through the lm3915). sorry about the mix up!
- #6
schip666!
- 595
- 0
AlephZero said:That's what "LM3915" on the circuit diagram means.
What specifically don't you understand?
I don't understand how I managed to miss that is what I don't understand...
- #7
davenn
Science Advisor
Gold Member
2023 Award
- 9,589
- 10,254
SammHunka said:Basically i just need help understanding what the reference dc voltage connected to the top LED is for, what the variable resistor is for, and basically how the overall circuit works (meaning how the output is created through the lm3915). sorry about the mix up!
the DC voltage connected to one side of ALL the leds is the + power supply for those LEDs
The variable resistor is to set the gain/level of the input to the chip so that you don't overdrive it. overdriving it could ...
a) damage the input to the chip
b) mean that ALL the LED's would be permanently lit up so you wouldn't have any meaningful variation in the LED display
Dave
- #8
SammHunka
- 3
- 0
Thank you dave and the rest of you guys! presenting it to my peers tomoro so i will check back with how it went! much thanks!
1. What is a LED Audio VU meter circuit?
A LED Audio VU meter circuit is an electronic circuit that detects and measures the audio signal level and displays it using a series of LEDs. It is commonly used in audio equipment such as amplifiers, mixers, and music players to provide a visual representation of the audio signal's strength.
2. How does a LED Audio VU meter circuit work?
The circuit works by converting the audio signal from the input source into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and filtered. The filtered signal is then used to control the brightness of the LEDs, with the brightness increasing as the audio signal's strength increases.
3. What are the components needed to build a LED Audio VU meter circuit?
The basic components needed for a LED Audio VU meter circuit include resistors, capacitors, transistors, LEDs, and a power source. Additional components such as op-amps, diodes, and potentiometers may also be used depending on the specific design.
4. What are the applications of a LED Audio VU meter circuit?
A LED Audio VU meter circuit is commonly used in audio equipment to provide a visual representation of the audio signal's strength. It can also be used in recording studios and live performances to monitor and adjust audio levels. Additionally, it can be used in DIY projects for audio visualization or as a fun electronic display.
5. Are there any variations of a LED Audio VU meter circuit?
Yes, there are various types of LED Audio VU meter circuits, including bar graph, dot matrix, and dot/bar hybrid designs. Some circuits may also incorporate features such as peak hold, adjustable sensitivity, and different color LEDs. The specific design and components used may vary based on the desired functionality and application.
Similar threads
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 789
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 26
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 24
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 857
Share: