- #1
WetFork
- 6
- 0
I have been given this problem, I've simplified it down to a total resistance however I'm unsure on whether I have done it correctly. Any pointers would be nice, thanks.
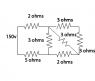
First of all I added the two resistors together in the top right as they are series. I then used that product with the (R1*R2)/(R1+R2) with the diagonal resistor as they are in parallel. I then added that up with the one in the bottom right as they are now in series. Used that product with the parallel formula with the one in the middle and then added the last two on the left.
My answer I got was 8.72 ohms total resistance, have I correctly done this?
Thanks for any help provided
First of all I added the two resistors together in the top right as they are series. I then used that product with the (R1*R2)/(R1+R2) with the diagonal resistor as they are in parallel. I then added that up with the one in the bottom right as they are now in series. Used that product with the parallel formula with the one in the middle and then added the last two on the left.
My answer I got was 8.72 ohms total resistance, have I correctly done this?
Thanks for any help provided