- #1
aim1nonly
- 1
- 0
Hi guys,
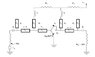
I am trying to find a way to calculate biasing network for the attached circuit.
Basically I need to find R1 and R2 values for operating point of I0 = 10mA and V0 = 10V and Vs = 16V.
DC current gain is assumed to be hFE=80.
How do you calculate R1 and R2 based on these info? Please let me know.
Thanks in advance!
I am trying to find a way to calculate biasing network for the attached circuit.
Basically I need to find R1 and R2 values for operating point of I0 = 10mA and V0 = 10V and Vs = 16V.
DC current gain is assumed to be hFE=80.
How do you calculate R1 and R2 based on these info? Please let me know.
Thanks in advance!