- #1
Fidelius
- 1
- 0
Hi PhysicsForums.
I have a question. I was looking through a manual for an industrial grade PC, which is fanless, with the CPU mounted directly onto the chassis which is practically one large heatsink.
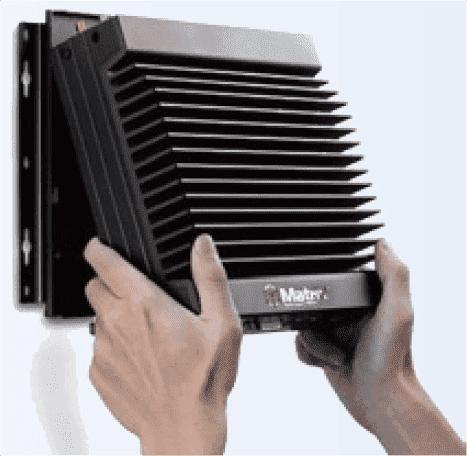
When considering side-mount applications for this PC, I noticed that the manual had a picture of the PC being mounted with the heatsink fins running horizontally, rather than vertically:

I thought - surely convection would be much more effective if the fins were running vertically, then cool air would be coming in from the bottom and escaping from the top:
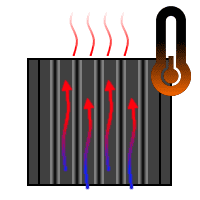
...otherwise the air would have no obvious path of escape:
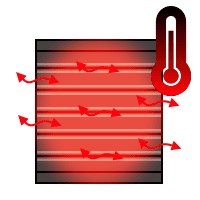
... or is the difference between the two side-mount orientations negligible? Thoughts?
Obviously sitting flat is the optimum orientation, but I'm just considering the wall-mounting options here.
I have a question. I was looking through a manual for an industrial grade PC, which is fanless, with the CPU mounted directly onto the chassis which is practically one large heatsink.
When considering side-mount applications for this PC, I noticed that the manual had a picture of the PC being mounted with the heatsink fins running horizontally, rather than vertically:
I thought - surely convection would be much more effective if the fins were running vertically, then cool air would be coming in from the bottom and escaping from the top:
...otherwise the air would have no obvious path of escape:
... or is the difference between the two side-mount orientations negligible? Thoughts?
Obviously sitting flat is the optimum orientation, but I'm just considering the wall-mounting options here.