- #1
BurnIt0017
- 25
- 0
Greetings, I have been working on a permanent magnet alternator, axial flux configuration.
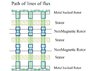
It has been configured with vertically staked stators and rotors. The traditional fabrication technique the stator is one large diameter with a large diameter magnet rotor above and the below the stator.
The vertical configuration that I am use requires ½ the magnets then the traditional fabrication method.
1 Can the vertically stacked PMA produce the same current and voltage output as a traditional PMA at the same RPM? Both are fabricated with the same coils and have the same air gap. The PMA’s are fabricated with same magnets, the only differences are the vertically stacked configuration has ½ the magnet count.
It has been configured with vertically staked stators and rotors. The traditional fabrication technique the stator is one large diameter with a large diameter magnet rotor above and the below the stator.
The vertical configuration that I am use requires ½ the magnets then the traditional fabrication method.
1 Can the vertically stacked PMA produce the same current and voltage output as a traditional PMA at the same RPM? Both are fabricated with the same coils and have the same air gap. The PMA’s are fabricated with same magnets, the only differences are the vertically stacked configuration has ½ the magnet count.