- #1
arperidot
- 1
- 0
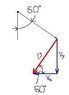
The minute hand of a clock is 5.5 cm long. What is average velocity vector for the tip of the hand during the interval from the hour to 20 minutes past the hour, expressed in a coordinate system with they-axis toward noon and x-axis toward 3 o'clock? (Answer in terms of i-hat and j-hat components please)