- #1
itlivesthere
- 4
- 0
Homework Statement
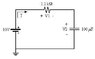
Calculate the steady state values of the current, voltages V1 and V2 (defined by a period of time greater than five time constants). (Circuit in ASCII below).
+ V1 -
_________Res (1.2 kΩ)___________
| I => |
| | +
| + |
E 10V Cap (100 μF) V2
| - |
| | -
|------------------------------------------|
GND
Homework Equations
τ=RC, E=IR, V= Vsource(1-e^-t/RC)
The Attempt at a Solution
I'm a novice at electrical/electronics engineering, but I'm eager to learn all I can. Correct me if I'm wrong with the following:
I determined the time constant of this circuit is .12 seconds. As I understand correctly, it takes approximately five time constants for a capacitor to charge up to its steady-state voltage, which in this case equates to .6 seconds.
The current after it crosses the 1.2 kΩ resistor is calculated as 8.3 mA.
I'm very much stuck at this point... any advice?