- #1
stockill92
- 1
- 0
Hello, new to these forums
I'm trying to complete a basic thermodynamics problem, calculating the thermodynamic temperature of a gas immersed in water at triple point.
The problem begins with a table of pressures at varying temperatures of a gas under pressure P, and pressure P(tp) - triple point pressure.
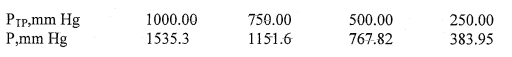
Now, I know the following equation;
So I have calculated the average value of P/PTP as 1.53555
But I also have access to a solution to this problem, and in the solution an extra step is also taken:
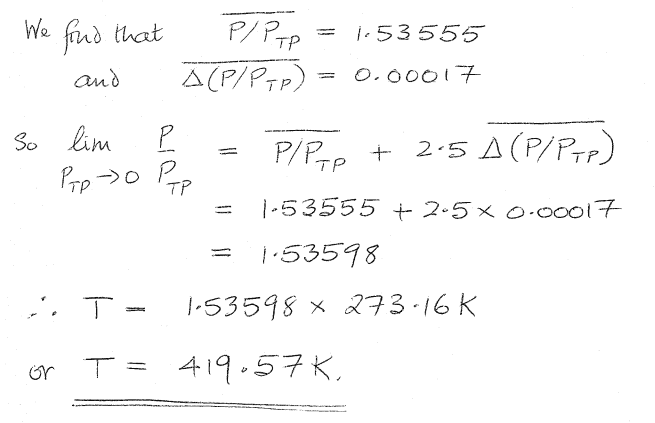
I don't understand the source of the 2.5 * avg change between P and P(tp). Where has this come from? Why is it necessary?
Thanks
I'm trying to complete a basic thermodynamics problem, calculating the thermodynamic temperature of a gas immersed in water at triple point.
The problem begins with a table of pressures at varying temperatures of a gas under pressure P, and pressure P(tp) - triple point pressure.
Now, I know the following equation;
T=LIMPTP→0P/PTP * 273.16
So I have calculated the average value of P/PTP as 1.53555
But I also have access to a solution to this problem, and in the solution an extra step is also taken:
I don't understand the source of the 2.5 * avg change between P and P(tp). Where has this come from? Why is it necessary?
Thanks