- #1
majormuss
- 124
- 4
I am trying to find the density, scale radius and normal radius of the milky way's halo. But these things are pretty hard to find. I want to find them so I can input them into the NFW profile:
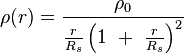
The Milky Way's halo has an estimated size of 300,000 light-years. This means that it extends 300,000 light-years from the center of the galaxy.
The Milky Way's halo is estimated to contain about 10% of the galaxy's total mass. This is mostly made up of dark matter, which cannot be directly observed but can be detected through its gravitational effects.
The shape of the Milky Way's halo is not well-defined and is still a subject of debate among scientists. Some theories suggest that it may be spherical, while others propose it to be more elongated or even flattened.
The Milky Way's halo exerts a gravitational force on stars and gas in the galaxy, causing them to orbit around the galactic center. It also influences the formation and evolution of the galaxy by regulating the flow of gas and the formation of new stars.
The origin of the Milky Way's halo is still a topic of ongoing research. It is believed to have formed from the merging of smaller galaxies and the accretion of gas and stars from the surrounding environment. The exact formation process is still not fully understood and is a subject of ongoing study.