You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Ferromagnetism: Definition and 35 Discussions
Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type and is responsible for the common phenomenon of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism—paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism—but the forces are usually so weak that they can be detected only by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is "the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are the materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel and most of their alloys, and some compounds of rare earth metals.
Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks, and nondestructive testing of ferrous materials.
Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically "soft" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically "hard" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from "hard" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico, and ferrimagnetic materials such as ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a strong magnetic field during manufacture to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. "Hard" materials have high coercivity, whereas "soft" materials have low coercivity. The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.
View More On Wikipedia.org
Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks, and nondestructive testing of ferrous materials.
Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically "soft" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically "hard" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from "hard" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico, and ferrimagnetic materials such as ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a strong magnetic field during manufacture to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. "Hard" materials have high coercivity, whereas "soft" materials have low coercivity. The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Classical magnetic dipole-dipole interaction in iron
I'm having a bit of trouble with this exercise because, even if I understand the physics of the dipole-dipole interaction in an ideal classical system, I don't get to know how to approach this problem. I've got a few doubts about how this system would work. First of all, what would be the...- rogdal
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
J
I Broken symmetry in ferromagnetism
Hello, Today I found this paper and this one where P.W. Anderson says that there is no broken symmetry in ferromagnetism because the ground state is an eigenstate of the spin rotation operator. And so we don't have in this system Goldstone's mode for example. But I thought spin waves were...- jean194
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Broken Ferromagnetism Symmetry
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
T
Lenz's Rule and Ferromagnetism
Hi, In this video: , it shows someone with an aluminium ring next to an MRI scanner. He allows the ring to fall over and it falls slowly demonstrating Lenz's law. I understand this but was wondering what would happen if a ferromagnetic ring was used instead of the non-ferromagnetic aluminium...- TP9109
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
M
Momentum transfer between d-electrons and the nucleus in ferromagnetism?
If a copper wire is wound around a piece of iron, nickel or cobalt, and a voltage is applied to the wire, it takes a longer amount of time for the current to reach its maximum value, than if the iron were replaced with a different material, such as glass— a phenomenon known as inductance. My...- metastable
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
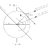
Apparent vanishing of (magnetic) potential energy
Dear all, I cannot figure out my mistake with this thought experiment: Consider a ferromagnetic material (e.g.iron) in a magnetic field - or just any iron anywhere, since the range of magnetic fields is infinite. Between the ferromagnetic material and (permanent) magnets potential energy is...- stockzahn
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
U
Saturation magnetization of iron as a function of temperature
Hi, I am looking for the temperature dependence of the saturation magnetization of Fe. Any help?- umby
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

Permanent Magnets Described by Magnetic Surface Currents - Comments
Charles Link submitted a new PF Insights post Permanent Magnets Explained by Magnetic Surface Currents Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.- Charles Link
- Thread
- Replies: 36
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
A
Calculating Magnetic Pole Strength: Guide to Theory & Experiment
Ok, I've spent lots of hours browsing the web and the library and still this question is burning. How can i calculate, whether it be experimentally or theoretically, the " pole strength" of a magnet. (I have read about the experiment where you divide the work it takes to turn a magnet around a...- Anthony physics
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
I Two Ferromagnets with Opposite Electron Spins
What happens when two ferromagnets with opposite electron spins interact with each other? Assuming the magnets are placed in conditions under the Curie temperature of the material, would their spins not change because the magnetic susceptibility is not high enough? Thank you.- Sahil Doshi
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electron Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
O
Ferromagnetism - thought problem
Hi! This might be a dum idea but here goes. Say you have 3 items. One weak magnet and two ferromagnetic materials of different susceptability. The magnet is strong enough to saturate the first material bot not the second. But since the saturated field in the first material is larger than that...- Onjii
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

How does diamagnetism originate?
For AP Physics or Chemistry, how do we explain the origin of magnetism, and diamagnetism? Saying that "Well, it's a quantum mechanical effect" or "it is a relativistic effect" isn't much help in explaining it's origin. Are there semi-classical explanations or analogies, that high school seniors... -
S
Using ferromagnetism in reinforced concrete
Hey there, I am currently majoring in civil engineering. A while ago when I was wondering about ferromagnetism an idea occurred to me: In reinforced concrete design adherence between structural steel and concrete is a very important feature. Simply, if we could enhance the adherence, this...- Semkan
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concrete Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-
S
Magnetic levitation using eddy current
Hi, I am working on an experiment to investigate the effect of electrical conductivity of the metals on the levitating force produced. Basically the concept is this: when a metal plate is placed on top of a solenoid (but not touching), as the a.c. flows in the solenoid the change in magnetic...- smokedvanilla
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Electrical Engineering
-
U
Curie-Weiss Paramagnetism susceptibility
Homework Statement (a) Show the curie-weiss behaviour. (b) Estimate ##\lambda## and ##B_e## and exchange energy.[/B] Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution Part(a) Since even when applied field is zero, ##B_{total} \neq 0## which gives rise to ##M\neq 0##. This is a fundamental...- unscientific
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
K
Ferromagnetism Modeling: Understanding the Basics and Finding a Mentor
Please,,I think that in ferromagnetism modelling most of ideas is discussed I want to have some plan of master how can I contact with some professor to achieve this purpose to know the right answer...- kkk777
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ferromagnetism Modeling
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Materials and Chemical Engineering
-
U
Magnetic Susceptibility and Curie Temperature
Homework Statement Part(a): Derive susceptibility Part(b): Find field experienced by neighbour. Part(c): State temperature range. What explains temperature dependence beyond curie temperature? Why is curie temperature so high? Part(d): In practice, measured magnetic moment is far lower than...- unscientific
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

Ferromagnetism in an iron disc
Homework Statement Attached. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution For the first part I determined the net magnetic dipole moment of the disc by calculating the number of moles the iron the disc comprises of and hence the number of atoms. Then, by making the assumption that 30%...- samjohnny
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Disc Ferromagnetism Iron
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
Generalising the Ising model to multiple spin values
My tutor asked us today to consider the partition function of the following model as an aside to our topic at the moment. I went to work out the maths of it today and I'm quite stuck for how the calculation can proceed. It's a 1d closed chain with some number, n, points. Each point has some...- TSRUser1234
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-

Mean-Field Approach to Ferromagnetism (Assistance with Calculations)
Homework Statement I am currently working as an intern in a research institute (I'm a 3rd yr undergrad) and my supervisor has asked me to create a simulation from a particular model - please see linked <http://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.69.045202> or attached paper. I...- vanoccupanther
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
S
Ferromagnetism and Work done by a bar magnet.
I was just doing a read-through of my freshman griffith's electrodynamics textbook ( I found my comprehension of electrodynamics slipping again ... always gets me edgy ) and I find my self flummoxed yet again. So he goes through an example of magnetic forces lifting a weight, and shows how it's...- siddharth5129
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
D
Ferromagnetism: Permanent Magnetic Force and Kinetic Energy
Can you explain me this: Ferromagnet has permanent magnetic force and can't lose it in the constant conditions, so if i put magnet and piece of the metal it will be pulled away from the magnet creating some kinetic energy. As energy can't be created, just transfered, so I don't understand who...- debeselis
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
D
Difference between paramagnetism and ferromagnetism
Homework Statement I've been asked to describe the difference between these two, but I'm a but confused. In my book, it says that paramagnetism is weaker than ferromagnetism, but I don't see why. If I'm not mistaken, both paramagnetism and ferromagnetism arise from the fact that you...- Denver Dang
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
F
Ferromagnetism for 3d, 4f metals
Why Fe, Co and Ni are ferromagnetic? what aspects of their electronic structure favors ferromagnetism? How 3d or 4f metals can be ferromagnetic and what is their origin of ferromagnetism?- fizikbrat
- Thread
-
- Tags
- 3d Ferromagnetism Metals
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
C
Ferromagnetism versus Paramagnetism
I know that the different magnetic properties arise from the spin of the electron, I also did some determinations whether a molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic (using MO theory), but I don't know how to make a difference between ferromagnetism and paramagnetism. Could someone explain it? And...- Chemist@
- Thread
- Replies: 27
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
D
Solving the Landau-Lifgarbagez-Gilbert Equation for Ferromagnetism
I'm trying to work out how fast I can switch an electromagnet's polarity, assuming I know the properties of the core's material. The magnetization dynamics are described by the Landau-Lifgarbagez-Gilbert equation (dM/dt = -ℽMxHeff + λMx(MxHeff), which is quite a chore to solve, seeing as it uses...- dorker
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
Ferromagnetism, what's happening in cylindrical magnets?
I've a question on ferromagnetism. I've been trying to simulating the field around a rod shape magnet, cylindrical in shape and N on one end and S on the other. I just wonder if one would expect the the B, the magnetic flux density, to be uniform in magnet. I used comsol to simulate and get...- soljiang
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
S
I've read that ferromagnetism is a quantum mechanical phenomenon and
I've read that ferromagnetism is a quantum mechanical phenomenon and have some questions: 1) Is it an example of quantum coherence, like laser light, superconductivity, etc.? 2) Since it depends on electron alignment amongst the iron atoms of the magnet, and since electrons have both...- sci-guy
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
S
Structural alignment in ferromagnetism
Is it enough/correct to say "the atoms are aligned" in a ferromagnet, or must you specify that "the electrons (or their spin) are aligned"?- sci-guy
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
U
Ferrimagnetism vs ferromagnetism
Hello All, I am trying to learn about the diffrerent types of magnetism and would like to know how we can tell the difference between ferri- and ferromagnetism? Are their any measurements which can distinguish unequivocally between the two types? Thank you for any help- username327
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
F
Questions on ferromagnetism and attraction
I have questions about magnetic attraction in both conceptual and application. I am not a physicist (medical background) so I may have insufficient understanding of the concepts involved, but any clarification would be helpful. Suppose I have a field source, such as a permanent magnet, and a...- FieldOpsGirl
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Attraction Ferromagnetism
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
B
Ferromagnetism, electrodynamics and field theory
Hi all, I'm a bit confused about ferromagnetism (and I've come to realize that I'm not the only one)! I'm currently studying electrodynamics and field theory in general to solidify my understanding of such, but permanent magnets and ferromagnetic materials seem to be often ignored in the...- Babcock McGee
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
B
Conduction electron ferromagnetism
Homework Statement We approximate the effect f exchange interactions among the conduction electrons if we assume that electrons with parallel spins interacti with each other with energy -V, and V is positive, while electrons with antiparallel spins do not interact with each other. (a) Show...- big man
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
P
Explaining paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and ferromagnetism
I have a short paper to write this weekend and my physics book doesn't do a very good job of explaining paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and ferromagnetism. Anyone know a good website that gives similarities and differences among those 3 types of magnetism? Thank you.- physics231
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-
P
Fields in ferromagnetism and proper range of atom size
When iron, cobalt and nickel are placed in weak fields they assume a large magnetic polarization. I was wondering if this weak field needs to be either diagmagnetic or paramagnetic field. My guess is that it is paramagnetic but not sure which paramagnets could be used. 'Weak field' is used...- Plastic Photon
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Atom Ferromagnetism Fields Range
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
S
How Do Magnetic Fields Influence Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Materials?
When a magnetic field is applied to a diamagnetic, the dipoles align opposite to the direction of the magnetic field. However, when a magnetic field is applied to a paramagnetic, the dipoles align to the same direction of the magnetic field. My professor mentioned in class that the...- SkyeSplash
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Ferromagnetism Phenomenon
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism