- #1
tarheelfan286
- 3
- 0
[SOLVED] circular motion and tension
I could do this easily if it weren't rotating or if it were one wire...but this is kicking my but.
Two wires are tied to a 340 g sphere. Both wires are 1m in length and attached to a pole at lengths of .5m below and above the sphere. The sphere revolves in a hori*zontal circle at a constant speed of 7.0 m/s. What is the tension in each of the wires?
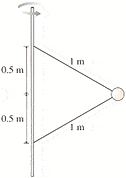
I could do this easily if it weren't rotating or if it were one wire...but this is kicking my but.
Two wires are tied to a 340 g sphere. Both wires are 1m in length and attached to a pole at lengths of .5m below and above the sphere. The sphere revolves in a hori*zontal circle at a constant speed of 7.0 m/s. What is the tension in each of the wires?