- #1
seiei
- 26
- 0
Homework Statement
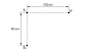
Two sources S1 and S2 of sound are situated 80cm apart in air, as shown in the image provided. The frequency of vibration can be varied. The two sources always vibrate in phase but have different amplitudes of vibration. A microphone M is situated a distance 100cm from S1 along a line that is normal to S1S2. As the frequency of S1 and S2 is gradually increased, the microphone M detects maxima and minima of intensity of sound.
The speed of sound in air is 330ms-1. The frequency of the sound from S1 and S2 is increased. Determine the number of minima that will be detected at M as the frequency is increased from 1.0kHz to 4.0kHz.
Homework Equations
Frequency=Velocity/Wavelength
(n-½)(λ/a) = x/D where λ is wavelength, x is separation between adjacent maxima and minima and D is the perpendicular distance from the zero order maximum.
The Attempt at a Solution
Using the two ranges of frequency 1.0kHz and 4.0kHz, the wavelengths must be between 8.25cm and 33cm but not sure what to do next. Any help would be greatly appreciated. Thank you.