- #1
Boccard
- 6
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Band structure of graphene and its energy dispersion.
Hello,
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Top-Graphene-nanoribbons-with-zigzag-left-and-armchair-right-edges-with-disordered_fig1_258105786
With what kx/ky values are these band structures plotted?
The energy dispersion of graphene is given by this
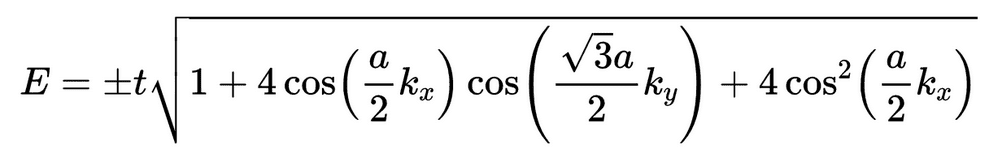
, yet I am confused to what kx/ky value choices I make to plot the graphs depicted in the link.
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Top-Graphene-nanoribbons-with-zigzag-left-and-armchair-right-edges-with-disordered_fig1_258105786
With what kx/ky values are these band structures plotted?
The energy dispersion of graphene is given by this
, yet I am confused to what kx/ky value choices I make to plot the graphs depicted in the link.