- #1
sinjid9
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
If mu = 0.2 find the maximum angle before slipping occurs
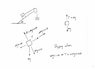
Diagram: A ramp in the shape of a right triangle that is 30 degrees above the horizontal. A mass is on the ramp and tied to it is a string that runs around the ramp to the vertical side of the ramp where another mass is held in the air.
Homework Equations
F(net)=ma
F(friction)=(mu)*(Normal Force)
The Attempt at a Solution
F(friction) = 0.2*(Normal Force)
F(net) = 0
F(friction)-(Fgravitytan(theta))=0
0.2F(gravity) - (Fgravitytan(theta)) = 0