- #1
PainterGuy
- 940
- 69
hi everyone,
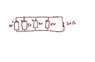
please look at attach picture.
in the circuit total current through 20 ohm resistor = sum of all currents delivered by each cell.
is this correct?
if one of battery is reversed then current of such a battery will be subtracted from the sum. is this correct?
i am grateful for any help you can come up.
cheers
please look at attach picture.
in the circuit total current through 20 ohm resistor = sum of all currents delivered by each cell.
is this correct?
if one of battery is reversed then current of such a battery will be subtracted from the sum. is this correct?
i am grateful for any help you can come up.
cheers