- #1
Shuff
- 4
- 0
I'm doing a project for my University. Making a design for a fish friendly dam structure that will let fish pass downstream without getting through the turbine.
Quick sketch:
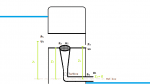
(1/2 u_1^2+p_1+gz_1 )_inlet=(1/2 u_2^2+p_2+gz_2 )_funnel+(1/2 u_3^2+p_3+gz_3 )_fishway
(1/2 u_2^2+p_2+gz_2 )_funnel=(1/2 u_4^2+p_4+gz_4 )_(turbine exit)
These are the two Bernoulli equations I have set up. Are they useable for this case?
If p1 is 20 meters under water surface, can one apply the basic 1 bar per 10meters, or will the water flow u1 play a major role on the p1?
p=F/A=(m⋅g)/A=(V⋅ρ⋅g)/A=(h⋅A⋅ρ⋅g)/A=ρ⋅g⋅h
Can p3 be assumed to be 1atm since it is so close to free air?
Also, how can p2 be calculated/assumed?
The problem I’m having is that I have too many unknowns. The u1 has to be assumed/given, but how can I calculate both u2 and u3. I guess the percentage of the area in the funnel and the fish tunnel ratio is not precise enough to calculate the ratio (funnel has ex. 80% more area than fishway so it has 4 times more flow). Since they are not located the same distance etc.
Quick sketch:
(1/2 u_1^2+p_1+gz_1 )_inlet=(1/2 u_2^2+p_2+gz_2 )_funnel+(1/2 u_3^2+p_3+gz_3 )_fishway
(1/2 u_2^2+p_2+gz_2 )_funnel=(1/2 u_4^2+p_4+gz_4 )_(turbine exit)
These are the two Bernoulli equations I have set up. Are they useable for this case?
If p1 is 20 meters under water surface, can one apply the basic 1 bar per 10meters, or will the water flow u1 play a major role on the p1?
p=F/A=(m⋅g)/A=(V⋅ρ⋅g)/A=(h⋅A⋅ρ⋅g)/A=ρ⋅g⋅h
Can p3 be assumed to be 1atm since it is so close to free air?
Also, how can p2 be calculated/assumed?
The problem I’m having is that I have too many unknowns. The u1 has to be assumed/given, but how can I calculate both u2 and u3. I guess the percentage of the area in the funnel and the fish tunnel ratio is not precise enough to calculate the ratio (funnel has ex. 80% more area than fishway so it has 4 times more flow). Since they are not located the same distance etc.