- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
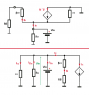
How Does Current Direction Affect BJT Impedance Calculations?
- Thread starter likephysics
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Bjt Calculation Impedance
In summary: This is just a convention and the actual direction of current does not affect the analysis.In summary, when analyzing the BJT equivalent circuit, the direction of current does not matter. This is because we are dealing with a small-signal model that is a mathematical abstraction of the real device. The input signal sees the BJT as a black box and can only perceive the load resistance, so the direction of current is irrelevant. The convention of choosing a positive direction for the input voltage and current is just for analysis purposes and does not impact the circuit's behavior.
Engineering news on Phys.org
- #2
- #3
likephysics
- 636
- 2
Why doesn't the direction of current really matter?
- #4
Jony130
- 627
- 138
Because we are dealing here with a BJT model not a real device.
And this small-signal model is nothing more then mathematical abstraction.
Our small-signal model describe the behavior of a BJT in "special condition".
We need properly DC bias the BJT into the linear region and apply low-frequency very small AC signal. And in this condition we create a small-signal model.
As for Rin = Vin/Iin our AC signal source can only see a resistance nothing more.
Because our Vin source apply voltage and supplies Iin current.
So our signal source see the BJT as a black box. So the only thing that our source is able to see is the load resistance .
And this small-signal model is nothing more then mathematical abstraction.
Our small-signal model describe the behavior of a BJT in "special condition".
We need properly DC bias the BJT into the linear region and apply low-frequency very small AC signal. And in this condition we create a small-signal model.
As for Rin = Vin/Iin our AC signal source can only see a resistance nothing more.
Because our Vin source apply voltage and supplies Iin current.
So our signal source see the BJT as a black box. So the only thing that our source is able to see is the load resistance .
- #5
vk6kro
Science Advisor
- 4,079
- 41
likephysics said:Why doesn't the direction of current really matter?
The input signal is AC, but for analysis purposes, we assume a direction for the input at one moment and then look at the directions of the currents in the circuit at that moment.
It is usual to take the input voltage and current as positive and then the other voltages and currents in the circuit depend on this.
1. What is a BJT?
A BJT, or bipolar junction transistor, is a type of semiconductor device that is commonly used in electronic circuits for amplification or switching purposes. It consists of three layers of doped material, namely the emitter, base, and collector, which form two pn junctions.
2. Why is impedance important in BJT circuits?
Impedance is an important characteristic of BJT circuits because it determines the voltage-current relationship in the circuit. It also affects the amplification and frequency response of the transistor. By understanding the impedance of a BJT circuit, we can design and analyze circuits more accurately.
3. How is BJT impedance calculated?
BJT impedance can be calculated using various methods, such as the h-parameter model, hybrid-pi model, or T-model. These models take into account the physical structure and characteristics of the transistor, such as its gain, input and output resistance, and capacitance. The specific method used for calculation may depend on the type of BJT circuit and the desired accuracy.
4. What factors affect BJT impedance?
The three primary factors that affect BJT impedance are the physical structure of the transistor, the operating conditions (such as biasing), and the frequency of the input signal. The size and doping of the layers in the BJT determine its inherent impedance, while the operating conditions and frequency can alter this impedance.
5. How can BJT impedance be controlled?
BJT impedance can be controlled by adjusting the operating conditions, such as the biasing voltage and current, or by using external components such as resistors and capacitors. The choice of these components can also influence the overall impedance of the circuit. Additionally, the physical structure of the transistor can be modified to change its impedance characteristics.
Similar threads
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 1K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 19
- Views
- 5K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 463
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 60
- Views
- 13K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 23
- Views
- 3K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 891
-
Electrical Engineering
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
Share: