- #1
ssjdbz101
- 6
- 0
Homework Statement
Could someone explain this problem a little better to me.
Problem:
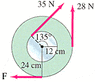
Calculate the net torque about the axle of the wheel shown in Fig. 8-39. Assume that a friction torque of 0.45 m·N opposes the motion and that F = 18.
*see attachment for picture.
I'm confused as how a wheel can have to forces (28N and 18N) on it in different directions on it at the same time.
Also, the 35N force looks like it is tangential to the smaller wheel, so do I have to use the 135 degrees in finding it's torque?
Torque equation: T=rFsin()
r=lever arm
F=force
Thanks in advance.