- #1
1msm
- 8
- 0
Hello everyone,
Here in below metal oxide semiconductor(MOS) capacitor,
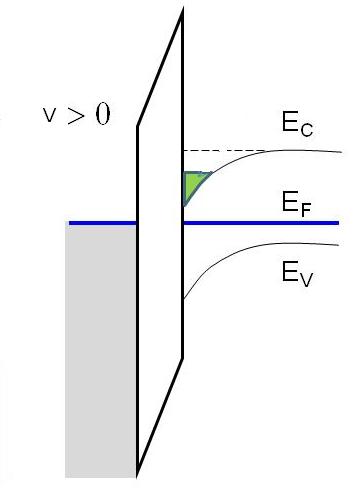
when we put positive potential on left side metal(gate), negative charge (electrons) get accumulated onto the right side semiconductor edge(as shown in green color), this results in bond bending in semiconductor and its conduction bond falls down.
So is the accumulating electrons potential energy is also falling down..??
and what happens to the next coming electrons..??
Here in below metal oxide semiconductor(MOS) capacitor,
when we put positive potential on left side metal(gate), negative charge (electrons) get accumulated onto the right side semiconductor edge(as shown in green color), this results in bond bending in semiconductor and its conduction bond falls down.
So is the accumulating electrons potential energy is also falling down..??
and what happens to the next coming electrons..??