- #1
Emara
- 2
- 0
Hello everyone,
Sorry I didn't have the time to rewrite the question, Can you help me with this?
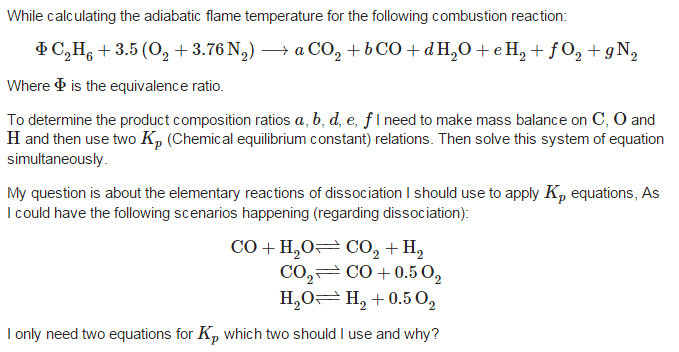
Sorry I didn't have the time to rewrite the question, Can you help me with this?
Chemical equilibrium for simultaneous dissociation reactions is a state in which the forward and reverse rates of dissociation reactions are equal, resulting in a constant concentration of reactants and products.
The equilibrium constant, or Keq, is determined by taking the ratio of the products to the reactants, with each concentration raised to the power of its coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
According to Le Chatelier's principle, an increase in temperature will favor the endothermic reaction, causing the equilibrium to shift to the right. Conversely, a decrease in temperature will favor the exothermic reaction and shift the equilibrium to the left.
No, the equilibrium constant is a characteristic of a chemical reaction at a specific temperature and does not change unless the temperature or concentrations of reactants and products change.
A catalyst does not affect the equilibrium constant, but it can increase the rate at which equilibrium is reached by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy.