- #1
Planobilly
- 440
- 105
Hi Guys,
The schematic
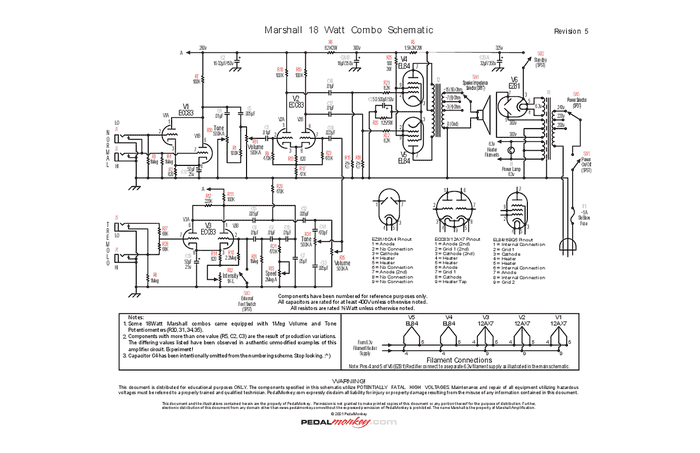
What do you think the effect of changing the value of the output tube cathode capacitor from 50uf to 250uf would be?
Also the original schematic showed 500K pots and other newer schematics show 1M pots. What do you think the effect of that change would be?
Next, assuming a 330 VDC plate voltage and a 100 ohm cathode resistor can you show me the process to predict the likely current flow. What I don't clearly understand is all the parameters that would affect the amount of current that would flow through the tube. Obviously the current is affected by the primary of the output transformer. What tube parameters also have an effect on the current?
Thanks,
Billy
The schematic
What do you think the effect of changing the value of the output tube cathode capacitor from 50uf to 250uf would be?
Also the original schematic showed 500K pots and other newer schematics show 1M pots. What do you think the effect of that change would be?
Next, assuming a 330 VDC plate voltage and a 100 ohm cathode resistor can you show me the process to predict the likely current flow. What I don't clearly understand is all the parameters that would affect the amount of current that would flow through the tube. Obviously the current is affected by the primary of the output transformer. What tube parameters also have an effect on the current?
Thanks,
Billy
Last edited: