- #1
girlwhoneedsmathhelp
- 7
- 3
Here is the question I'm struggling with (Q1) :
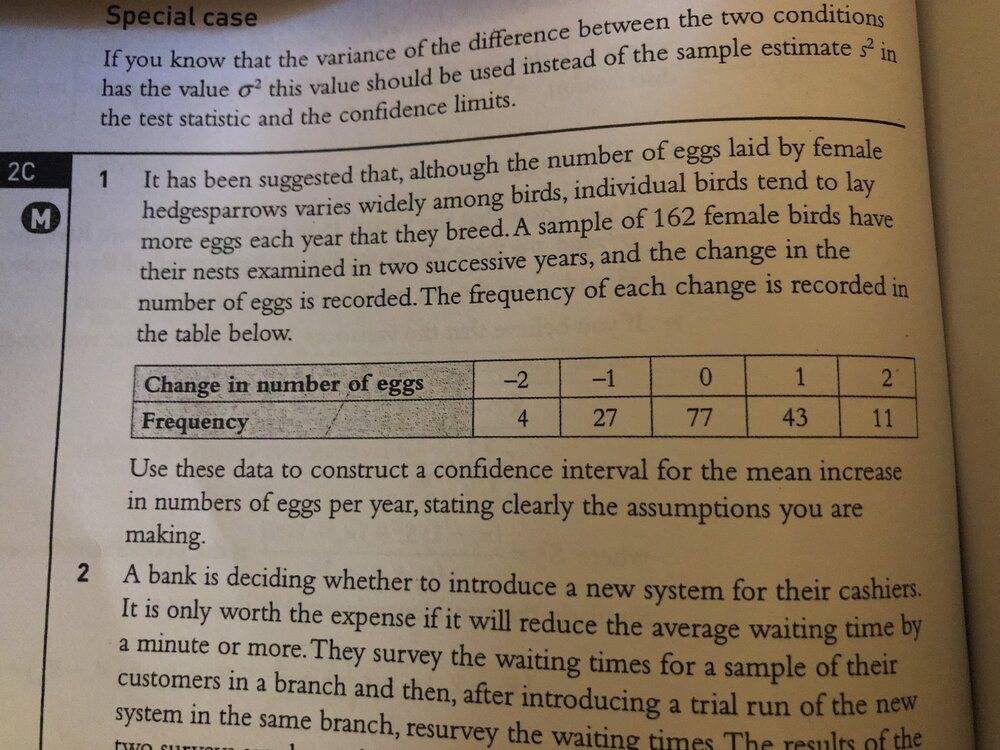
I just... I just don't understand what my first step is.
Whats my barx1 and barx2? (bar x = mean, x1 = subscript 1)
My thoughts on approaching this question :
barX1 - barX2 `~ N(u1-u2, sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2)
Find Z value when p = 0.975, z = + or - 1.96
Formula : (barx1-barx2)-z(root (sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2) < (u1-u2) < (barx1-barx2)-z(root (sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2)
Please help me! Thank you :)
I just... I just don't understand what my first step is.
Whats my barx1 and barx2? (bar x = mean, x1 = subscript 1)
My thoughts on approaching this question :
barX1 - barX2 `~ N(u1-u2, sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2)
Find Z value when p = 0.975, z = + or - 1.96
Formula : (barx1-barx2)-z(root (sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2) < (u1-u2) < (barx1-barx2)-z(root (sd1^2/n1 + sd2^2/n2)
Please help me! Thank you :)