- #1
Agalev
- 7
- 0
Please post this type of questions in HW section using the template. You have to show your attempts at solving the problem to receive help, this is a forum policy.
Hey,
I'm having a problem for some time finding out which of these materials are conjugated polymers and which aren't.
Can somebody please help me?

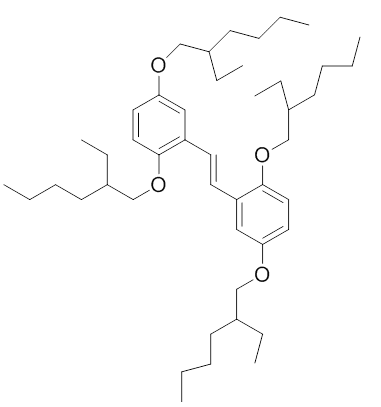
I'm having a problem for some time finding out which of these materials are conjugated polymers and which aren't.
Can somebody please help me?