- #1
Jozefina Gramatikova
- 64
- 9
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
modified Freidmann:
The Attempt at a Solution
for part b) I am not sure what to do as I am not sure what they mean by
Attachments
-
 upload_2019-3-13_11-38-49.png12.7 KB · Views: 756
upload_2019-3-13_11-38-49.png12.7 KB · Views: 756 -
 upload_2019-3-13_11-40-5.png10.6 KB · Views: 285
upload_2019-3-13_11-40-5.png10.6 KB · Views: 285 -
 upload_2019-3-13_11-42-39.png3.3 KB · Views: 517
upload_2019-3-13_11-42-39.png3.3 KB · Views: 517 -
 upload_2019-3-13_11-44-13.png2.7 KB · Views: 538
upload_2019-3-13_11-44-13.png2.7 KB · Views: 538 -
 upload_2019-3-13_11-45-9.png3 KB · Views: 520
upload_2019-3-13_11-45-9.png3 KB · Views: 520 -
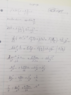 upload_2019-3-13_11-48-38.png61.7 KB · Views: 463
upload_2019-3-13_11-48-38.png61.7 KB · Views: 463 -
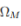 upload_2019-3-13_11-49-23.png505 bytes · Views: 338
upload_2019-3-13_11-49-23.png505 bytes · Views: 338 -
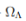 upload_2019-3-13_11-49-45.png474 bytes · Views: 362
upload_2019-3-13_11-49-45.png474 bytes · Views: 362 -
 54255729_158675795050187_2230191021470253056_n.jpg?_nc_cat=100&_nc_ht=scontent-lhr3-1.jpg11.7 KB · Views: 525
54255729_158675795050187_2230191021470253056_n.jpg?_nc_cat=100&_nc_ht=scontent-lhr3-1.jpg11.7 KB · Views: 525 -
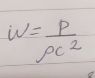 0133_2761327387625914368_n.jpg?_nc_cat=105&_nc_ad=z-m&_nc_cid=0&_nc_zor=9&_nc_ht=scontent-lhr3-1.jpg5.7 KB · Views: 434
0133_2761327387625914368_n.jpg?_nc_cat=105&_nc_ad=z-m&_nc_cid=0&_nc_zor=9&_nc_ht=scontent-lhr3-1.jpg5.7 KB · Views: 434