- #1
Peto
- 9
- 0
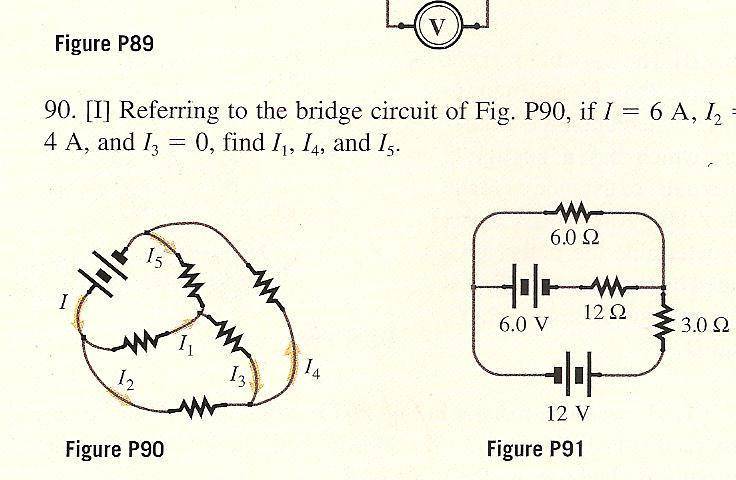
Referring to the bridge circuit of fig P90, if I=6A, I2=4A, and I3 = 0, find I1, I4, and I5.
 I did,
I did,
I1=2A
I4=4A
I5=2A
My logic being, since I is 6A, and I2 is 4A, I1 must be the difference, 2A. since I4 is coming from I2 and I3 it should be the sum, (0 + 4A = 4A). and I thought because I5 is coming from I1, it must be 2A.
Is this right?
Thanks for any help!
I1=2A
I4=4A
I5=2A
My logic being, since I is 6A, and I2 is 4A, I1 must be the difference, 2A. since I4 is coming from I2 and I3 it should be the sum, (0 + 4A = 4A). and I thought because I5 is coming from I1, it must be 2A.
Is this right?
Thanks for any help!