- #1
Omega0
- 205
- 51
Hi!
I would like to calculate the curvature for a surface S:R^2->R'3 numerically.
The problem: I simply have the surface as a mesh like you see in the image attached.
I calculated the linearly interpolated face normals in the nodes, too. You see the vectors.
Question: How would you calculate the Gauss curvature from this information?
Thanks!
Best wishes,
Jens
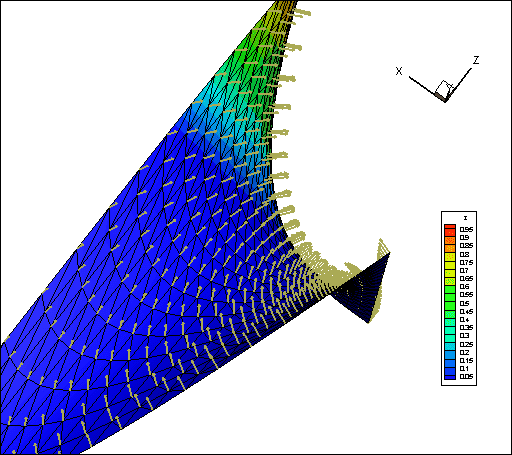
I would like to calculate the curvature for a surface S:R^2->R'3 numerically.
The problem: I simply have the surface as a mesh like you see in the image attached.
I calculated the linearly interpolated face normals in the nodes, too. You see the vectors.
Question: How would you calculate the Gauss curvature from this information?
Thanks!
Best wishes,
Jens