- #1
trinupab
- 1
- 0
Hi all,
I'm currently undergoing a masters of science course in Mechatronics Engineering. One of my core modules is Electrical Components. I'm stuck in understanding one of the key parts in this module. I've been asked to derive the Tangential and Normal forces of the rotor shown below.
I've been going through the notes and all i know is Force = I*L*Bsin(teta). Aside from that i find no connection in u0 (miu not)
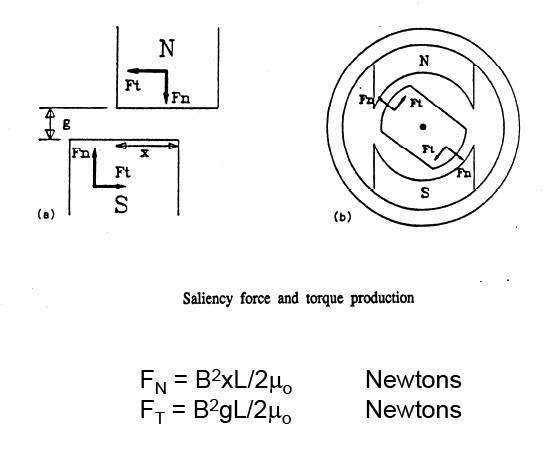
I would highly appreciate any feedback in this matter. I'm still new to this forum so i apologize for any mistakes caused.
Jay
I'm currently undergoing a masters of science course in Mechatronics Engineering. One of my core modules is Electrical Components. I'm stuck in understanding one of the key parts in this module. I've been asked to derive the Tangential and Normal forces of the rotor shown below.
I've been going through the notes and all i know is Force = I*L*Bsin(teta). Aside from that i find no connection in u0 (miu not)
I would highly appreciate any feedback in this matter. I'm still new to this forum so i apologize for any mistakes caused.
Jay