- #1
JasonHathaway
- 115
- 0
Hi everyone,
I'm new to transistors analyzing, and I need a way to correctly identify the voltages.
Let's take this circuit for example:
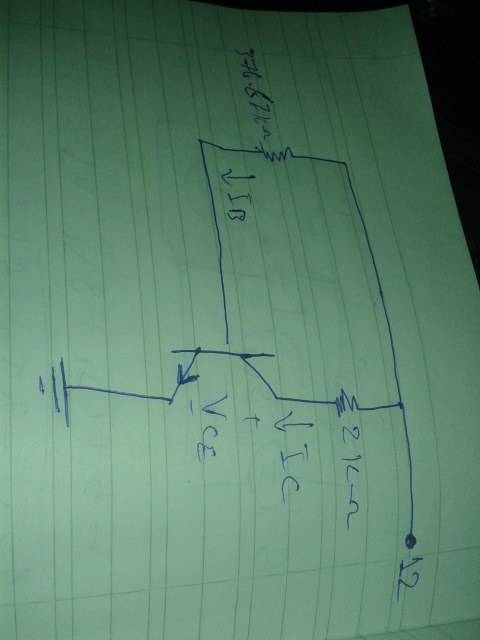
Assuming that the Emitter is the common element (The one with arrow which is connected to the ground), then VBE would be:
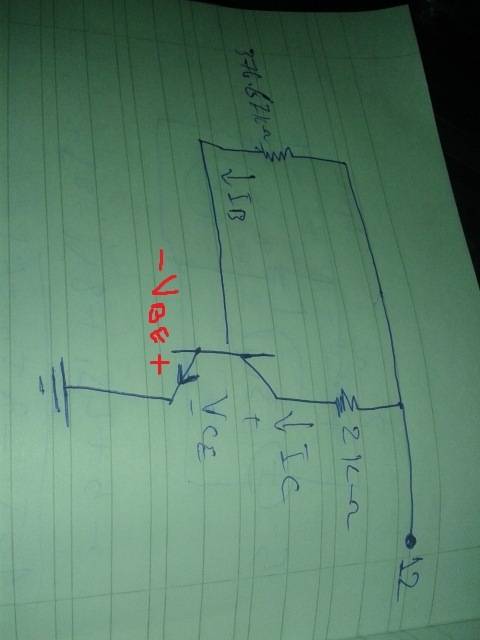
My questions are:
1- If I want to know the common element of the transistor, shall I look for the element that is directly connected to the ground?
2- For this circuit, I've VBE - VCE + VCB =0, On which basis I can get the these voltages?
I'm new to transistors analyzing, and I need a way to correctly identify the voltages.
Let's take this circuit for example:
Assuming that the Emitter is the common element (The one with arrow which is connected to the ground), then VBE would be:
My questions are:
1- If I want to know the common element of the transistor, shall I look for the element that is directly connected to the ground?
2- For this circuit, I've VBE - VCE + VCB =0, On which basis I can get the these voltages?