- #1
Mart1234
- 6
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
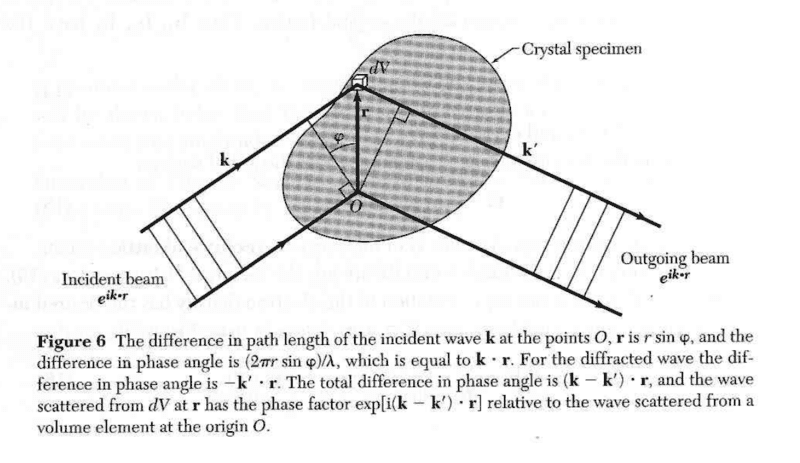
- Diffraction Condition derivation in Kittle's Introduction to Solid State Physics
I am going over the diffraction condition section in Kittle's Introduction to Solid State Physics physics and I am having a hard time understanding why the phase difference angle for the incident wave is positive while the phase angle difference for the diffracted wave is negative. Thank you for the help.
Last edited by a moderator: