- #1
student1938
- 91
- 1
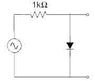
Sketch the output voltage as a function of time. The AC voltage source is [tex]V_{o}cos(\omega)t[/tex] with [tex]V_{o}[/tex] = 10V and [tex]\omega[/tex] = 2000rad/sec.
I have posted a diode circuit question in the attachment
Ok, I think it should be a sine curve with a 10 V amplitude but am not too sure about the period.
What would the output voltage look like if the position of the resistor and diode were switched?
Can someone help me with this please.
student1938
I have posted a diode circuit question in the attachment
Ok, I think it should be a sine curve with a 10 V amplitude but am not too sure about the period.
What would the output voltage look like if the position of the resistor and diode were switched?
Can someone help me with this please.
student1938
Attachments
Last edited: