- #1
lazyaditya
- 176
- 7
Homework Statement
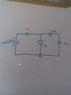
What will be the voltage v(t) across diode D1 ?
Homework Equations
The Figure is shown in the attachment.
The Attempt at a Solution
When there is a positive cycle D2 will be open circuit and capacitor 1 will be charged and diode D1 will be short circuited ,while in negative cycle the capacitor 2 will be charged D2 will be short circuited and D1 will be open so all the voltage across Capacitor 2 will be shown against D2 i guess but i am confused with waveform !