- #1
IamVector
- 98
- 9
- Homework Statement
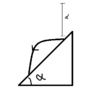
- An elastic ball is released above an inclined plane
(inclination angle α) at distance d from the plane. What is
the distance between the first bouncing point and the second?
Collisions occur without friction.
- Relevant Equations
- the answer I got is 8dsinα but given answer is 8dtanα
anything wrong with sol or my answer?