- #1
elemis
- 163
- 1
My professor, in his handout (picture below), says the following about this diagram :
I disagree with him partly. For [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] mixing is spontaneous and hence there solutions would be miscible. Hence at [itex]\beta=2.5[/itex] should we not expect the components to be fully miscible. ?
Following on from this logic; for [itex]\beta=3[/itex] the components are only miscible for [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] so the maxima represents a phase separation between the two components.
Who is correct ?
Additionally,the webpage below indicates that at the maxima there is one phase whilst at the minima there are two. Does this mean at the maxima the solutions are miscible ? If so, how can this be true given that [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] is positive and hence mixing is unfavourable ?
http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/~chdms/Teaching/Chemical_Interactions/page_17.htm
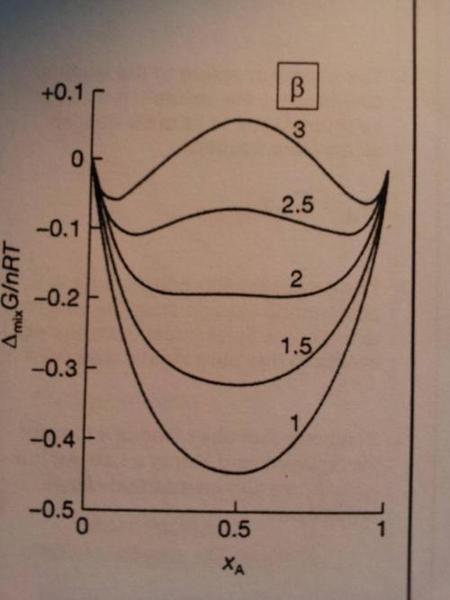
For [itex]\beta>+2[/itex] there are two minima and phase separation occurs driven
by unfavourable enthalpic interactions.
I disagree with him partly. For [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] mixing is spontaneous and hence there solutions would be miscible. Hence at [itex]\beta=2.5[/itex] should we not expect the components to be fully miscible. ?
Following on from this logic; for [itex]\beta=3[/itex] the components are only miscible for [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] so the maxima represents a phase separation between the two components.
Who is correct ?
Additionally,the webpage below indicates that at the maxima there is one phase whilst at the minima there are two. Does this mean at the maxima the solutions are miscible ? If so, how can this be true given that [itex]\Delta_{mix} G/nRT<0[/itex] is positive and hence mixing is unfavourable ?
http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/~chdms/Teaching/Chemical_Interactions/page_17.htm
Last edited by a moderator: