- #1
Swapnil Das
- 15
- 6
I am a tenth grader, and a newbie to Advanced Calculus. While working out problems sets for Gauss's Law, I encountered the following Surface Integral:
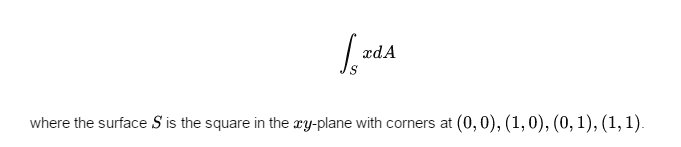 I couldn't attempt anything, having no knowledge over surface integration. So please help.
I couldn't attempt anything, having no knowledge over surface integration. So please help.