- #1
scanferr
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
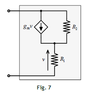
R1 = 1K Ohm
R2= 50K Ohm
gM = 100mA/V
I should find the equivelent resistor seen from the two terminals on the left
Homework Equations
Nodes equations, Ohm's law.
The Attempt at a Solution
So, I started by putting a test voltage source on the left but I end up with 2 variables on the equivalent resistor equation that I can't be able to solve.
I did Circuit analysis last year, which I passed but now I'm a bit rusty with this. Anyone can help me?