- #1
anhnha
- 181
- 1
I am having a hard time understanding flat band voltage in MOS capacitor.
Please see the picture below about MOS capacitor.
Q0 is a fixed effective charge at the surface between oxide and semiconductor and it is positive here.
The voltage across the oxide caused by the fixed charge ψox = -Q0/Cox.
So we need to use an external voltage to cancel this voltage ψox.
What I don't get here is the direction of external voltage for cancelling ψox.
As you can see from the picture, it has the same direction as ψox.
Should it be in the opposite direction so ψox can be cancelled?
Thank you.
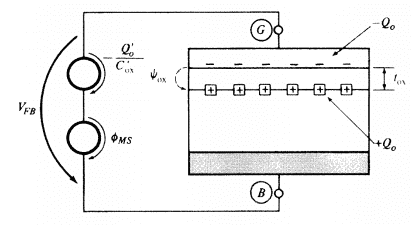
Please see the picture below about MOS capacitor.
Q0 is a fixed effective charge at the surface between oxide and semiconductor and it is positive here.
The voltage across the oxide caused by the fixed charge ψox = -Q0/Cox.
So we need to use an external voltage to cancel this voltage ψox.
What I don't get here is the direction of external voltage for cancelling ψox.
As you can see from the picture, it has the same direction as ψox.
Should it be in the opposite direction so ψox can be cancelled?
Thank you.