- #1
xzibition8612
- 142
- 0
Homework Statement
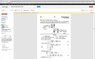
See attachment.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Equations (1) and (2) describe this gear train system. I'm confused about them.
For (1):
If I rewrite it (∑F=0 format) I get:
T-T1-Jθ''-Bθ' = 0
The figure clearly shows θ1 positive spinning towards the bottom. Why then is T1 negative if it is spinning in the same direction as θ1? I understand the inertia and damping is always opposite to the defined positive direction.
For (2):
T2-TL-Jθ''-Bθ' = 0
Since the figure doesn't show the direction TL is going, why is it negative?
Also why is there a T1 and T2 if I only apply a load T? Shouldn't it just be T-Jθ''-Bθ' = 0 ? Where did T1 and T2 come from if I only applied T? And what exactly is a load torque?
Now I'm thinking isn't it physically impossible for a single shaft to have two torques going in opposite directions?
I'm obviously very confused on this. Any help would be appreciated.