- #1
NW8800
- 16
- 0
Hey,
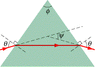
I have a problem.,. I am trying to figure out smallest angle of incidence θ for which a ray can enter the left face of the prism (seen in the pic below) and exit the right face.
The infomation I have:
The isosceles prism has apex angle φ = 56.1° and index of refraction n = 1.42
Diagram:
http://img520.imageshack.us/img520/5857/fig3355xp0.gif
Can someone giver me an answer on this?
Thanks,
NW
I have a problem.,. I am trying to figure out smallest angle of incidence θ for which a ray can enter the left face of the prism (seen in the pic below) and exit the right face.
The infomation I have:
The isosceles prism has apex angle φ = 56.1° and index of refraction n = 1.42
Diagram:
http://img520.imageshack.us/img520/5857/fig3355xp0.gif
Can someone giver me an answer on this?
Thanks,
NW
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: