- #1
r12214001
- 24
- 2
- Homework Statement
- HF molecular orbital
- Relevant Equations
- HF molecular orbital
In figure. Why F use 2P rather than 2S to bonding in HF MO model.
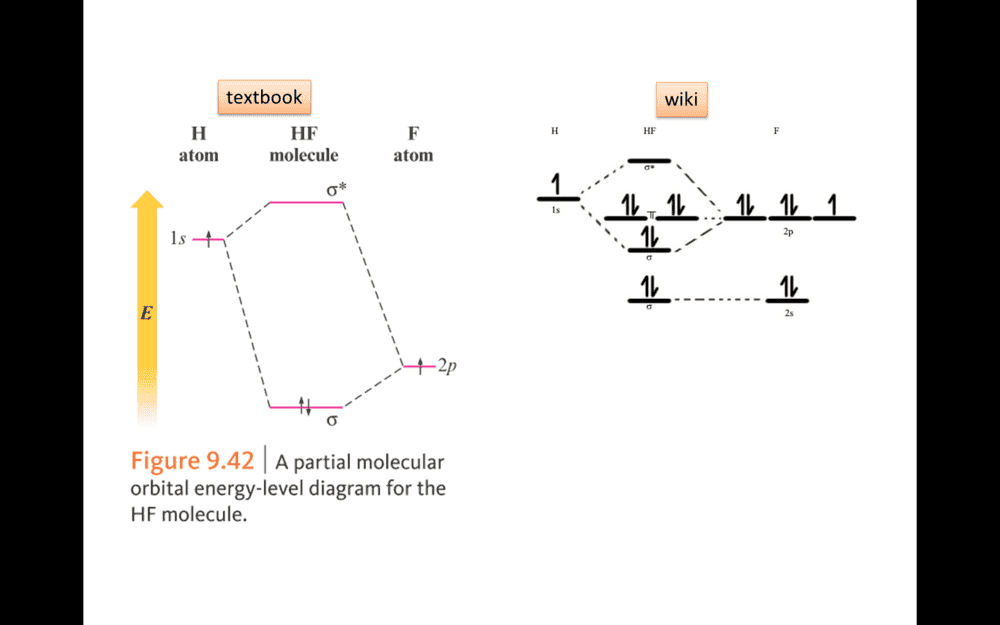
1S2 2S2 2P5Borek said:What is the electron configuration of a free F atom?
OK i get it. I should never use hybridization to account for MO theory.chemisttree said:Can you bond using suborbitals that are already filled?
The 2p orbitals of F and the 1s orbital of H have similar energies, making them a good match for bonding. Additionally, the electronegativity difference between F and H leads to a large dipole moment, making it favorable for the electron to be closer to the more electronegative F atom.
The HF molecular orbital model predicts a shorter bond length than the traditional Lewis dot structure model. This is because the molecular orbital model takes into account the overlap of atomic orbitals, which results in a stronger bond.
Yes, the HF molecular orbital model accurately predicts the bond strength of HF. This model takes into account the overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in a stronger bond compared to the Lewis dot structure model.
The Lewis dot structure model only considers the valence electrons of the atoms involved, while the HF molecular orbital model takes into account the overlap of atomic orbitals and predicts the distribution of all electrons in the molecule.
Yes, the HF molecular orbital model can be applied to other diatomic molecules. However, it becomes more complex when applied to larger molecules with more atoms and orbitals.