- #1
GeneralOJB
- 42
- 0
I need to find the moment of inertia of a sphere of radius ##r## and mass ##m## about an axis through it's centre. I've already done it and got the correct answer of ##\frac{2}{3}mr^2## however I have tried doing it using a different method to see if I get the same answer, but I don't, and I don't know why.
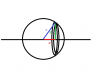
See the image attached.
The moment of inertia of one of the hoops is ##\displaystyle\frac{m}{4\pi r^2}\times 2\pi y \delta x\times y^2##.
##x^2+y^2=r^2## so I just need to evaluate ##\displaystyle\int_{-r}^r \frac{m}{4\pi r^2}\times 2\pi (r^2-x^2)^{3/2}\,\mathrm{d}x##
But I don't get the right answer.
See the image attached.
The moment of inertia of one of the hoops is ##\displaystyle\frac{m}{4\pi r^2}\times 2\pi y \delta x\times y^2##.
##x^2+y^2=r^2## so I just need to evaluate ##\displaystyle\int_{-r}^r \frac{m}{4\pi r^2}\times 2\pi (r^2-x^2)^{3/2}\,\mathrm{d}x##
But I don't get the right answer.
Attachments
Last edited: