- #1
mateomy
- 307
- 0
A 2.0 kg mass and a 3.0 kg mass are on a horizontal frictionless surface, connected by a massless spring with spring constant k=140N/m. A 15 N force is applied to the larger mass, as a shown (see picture). How much does the spring stretch from its equilibrium length?
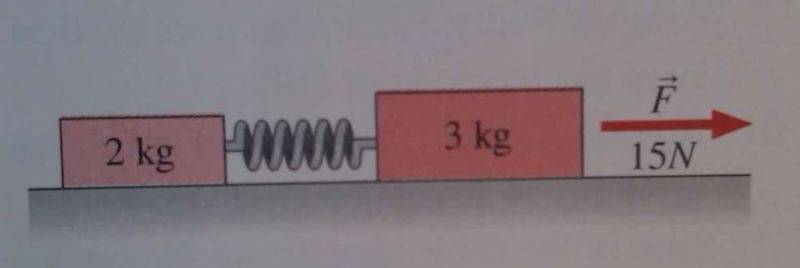
I've solved this problem -the answer is 4.28cm- but I had to do it using the force on the smaller of the masses (2 kg). My question is why I have to take it from that mass? Why couldn't you just find it from the 3 kg mass, by just taking the initial 15 N force as proportional to the Force of the spring? If you do this the book says that answer is wrong. The physical interpretation of WHY we have to to find it from the 2kg force is eluding me.
I've solved this problem -the answer is 4.28cm- but I had to do it using the force on the smaller of the masses (2 kg). My question is why I have to take it from that mass? Why couldn't you just find it from the 3 kg mass, by just taking the initial 15 N force as proportional to the Force of the spring? If you do this the book says that answer is wrong. The physical interpretation of WHY we have to to find it from the 2kg force is eluding me.