- #1
Mins
- 16
- 0
How a cube(a die) rolls(rolling motion help)
I want to show how a cube bounces and rolls when dropped from a slope(45 degrees).
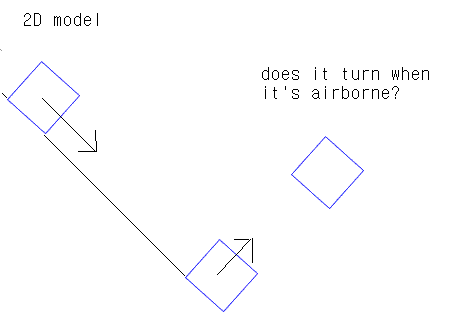
I'm trying to make this problem as easy as possible, so I've ruled out air current.
How will it bounce? Think I need to use 'e'(elasticity)(which is roughly 0.3)...
Then, I don't understand why it rolls when it's airborne... Does it roll at all? Did I miss something?
Another thing that bothers me is it's rolling motion when it's not bouncing up and down...
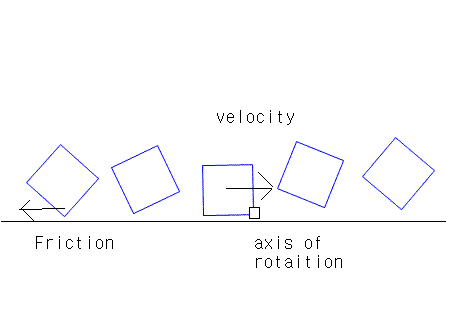 (Not sure of it and don't know what determines rolling friction)
(Not sure of it and don't know what determines rolling friction)
Where does the axis of the die lie?
and what is conserved, and what isn't?
extra)http://director-online.com/buildArticle.php?id=1075#dice
I want to show how a cube bounces and rolls when dropped from a slope(45 degrees).
I'm trying to make this problem as easy as possible, so I've ruled out air current.
How will it bounce? Think I need to use 'e'(elasticity)(which is roughly 0.3)...
Then, I don't understand why it rolls when it's airborne... Does it roll at all? Did I miss something?
Another thing that bothers me is it's rolling motion when it's not bouncing up and down...
Where does the axis of the die lie?
and what is conserved, and what isn't?
extra)http://director-online.com/buildArticle.php?id=1075#dice
Last edited: