- #1
arcTomato
- 105
- 27
- Homework Statement
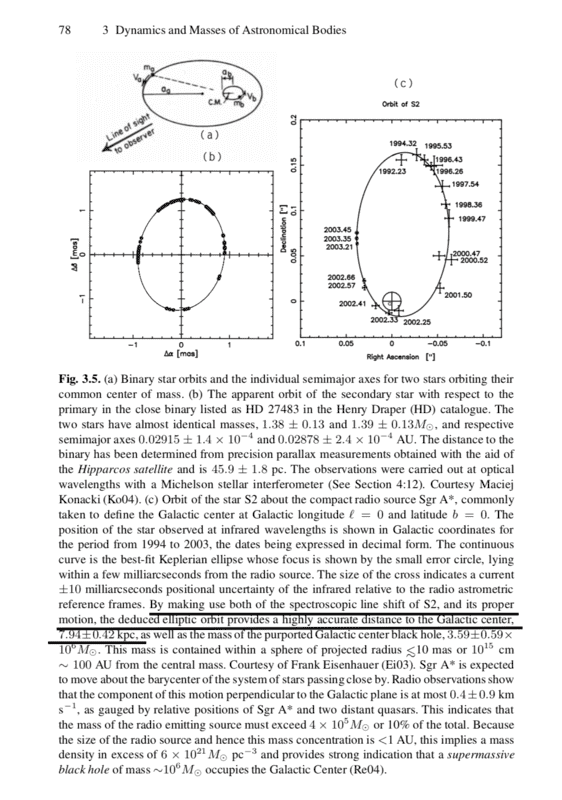
- We can use "spectroscopic line shift of S2" and "its proper motion", but I don't have any idea what dose this sentences mean.
please show me details!!
- Relevant Equations
- spectroscopic line shift
Problem Statement: We can use "spectroscopic line shift of S2" and "its proper motion", but I don't have any idea what dose this sentences mean.
please show me details!
Relevant Equations: spectroscopic line shift
please show me details!
Relevant Equations: spectroscopic line shift