- #1
LUFER
- 4
- 0
I'm having trouble finding in the literature specifically about the porous silicon process using the dry method instead of the more common wet method that is used.
wet process
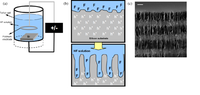
Using porous silicon to promote wet thermal oxidation uses the process electrochemically will allow water molecules to diffuse into it. Wet oxide is often used for oxide growth. So that the structure (cavities) does not collapse after using the previously mentioned process or remove that PENTAN.
Example: See the photo in attachment 01
dry process
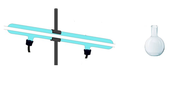
If it refers to the dry process, I can't find anything profound in the literature, it just cites the case. I would need to understand how this process works, the little I understood is that it uses two flasks where there is a cylindrical flask where there is an inlet and an outlet and the other flask where the Porous Silicon is used. If anyone can help me where I can find the literature.
Example: See the photo in attachment 02
wet process
Using porous silicon to promote wet thermal oxidation uses the process electrochemically will allow water molecules to diffuse into it. Wet oxide is often used for oxide growth. So that the structure (cavities) does not collapse after using the previously mentioned process or remove that PENTAN.
Example: See the photo in attachment 01
dry process
If it refers to the dry process, I can't find anything profound in the literature, it just cites the case. I would need to understand how this process works, the little I understood is that it uses two flasks where there is a cylindrical flask where there is an inlet and an outlet and the other flask where the Porous Silicon is used. If anyone can help me where I can find the literature.
Example: See the photo in attachment 02