- #1
xsgx
- 29
- 0
The problem:
A simple random sample of 1862 births of Chinese babies resulted in a mean birth weight of 3171 g and a standard deviation of 428 g
(based on “Comparison of Birth Weight Distributions between Chinese and Caucasian Infants,” by Wen et al., American Journal of Epidemiology, Vol.172, No 10). Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean birth weight of Chinese babies is less than the mean birth weight of 3369 g for Caucasian babies.
The attempted solution:
The null hypothesis is that the mean weight of Caucasian babies is the same as the mean weight for Chinese babies Ho: M = 3369, and the alternative hypothesis is that the mean weight for Chinese babies is less so H1: M<3369. For the first step I calculated the test statistic for the student t distribution because the standard deviation of the population is not known;using these values, sample mean=3171, Population mean = 3369(the mean weight in grams for the population of Caucasian babies because we are comparing the mean weight of the Chinese baby sample to the Caucasian baby population mean weight), the sample standard deviation 428, and the sample size 1862
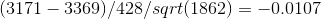 :which gave me a test statistic score T=-0.0107. I used the traditional method of using critical values. With a significance level of .01 and the hypothesis test being left tailed because the alternative hypothesis has a “less than” sign the critical value I calculated using statdisk was T=-2.33. Because the test statistic -0.0107 is far above that critical value I failed to reject the null hypothesis that M(Mean weight for Chinese babies)= 3369 (Mean weight for Caucasian babies).
:which gave me a test statistic score T=-0.0107. I used the traditional method of using critical values. With a significance level of .01 and the hypothesis test being left tailed because the alternative hypothesis has a “less than” sign the critical value I calculated using statdisk was T=-2.33. Because the test statistic -0.0107 is far above that critical value I failed to reject the null hypothesis that M(Mean weight for Chinese babies)= 3369 (Mean weight for Caucasian babies).
A simple random sample of 1862 births of Chinese babies resulted in a mean birth weight of 3171 g and a standard deviation of 428 g
(based on “Comparison of Birth Weight Distributions between Chinese and Caucasian Infants,” by Wen et al., American Journal of Epidemiology, Vol.172, No 10). Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the mean birth weight of Chinese babies is less than the mean birth weight of 3369 g for Caucasian babies.
The attempted solution:
The null hypothesis is that the mean weight of Caucasian babies is the same as the mean weight for Chinese babies Ho: M = 3369, and the alternative hypothesis is that the mean weight for Chinese babies is less so H1: M<3369. For the first step I calculated the test statistic for the student t distribution because the standard deviation of the population is not known;using these values, sample mean=3171, Population mean = 3369(the mean weight in grams for the population of Caucasian babies because we are comparing the mean weight of the Chinese baby sample to the Caucasian baby population mean weight), the sample standard deviation 428, and the sample size 1862
Last edited by a moderator: