- #1
Dell
- 590
- 0
the queen posted truss in the picture consists of the beam ABCD, compression members BE CF amd the cable AEFD, a stress analysis under the uniform load q is required. outline an analysis procedure, state the effects you would ignore and why.
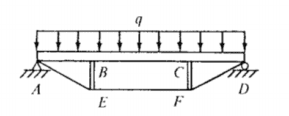
i am not sure what i am meant to be doing here, this is part of an assignment dealing with castiglianos 2nd theorem,. what is the analysis procedure? do they mean how would i go about finding the inner forces?
as far as effects to ignore, i would ignore the axial and shearing force in the beam ABCD, is this correct as i assume theirs to be negligible compared to the moment's energy.
can a cable have an internal shearing force and moment or also only axial forces( tension)
i am not sure what i am meant to be doing here, this is part of an assignment dealing with castiglianos 2nd theorem,. what is the analysis procedure? do they mean how would i go about finding the inner forces?
as far as effects to ignore, i would ignore the axial and shearing force in the beam ABCD, is this correct as i assume theirs to be negligible compared to the moment's energy.
can a cable have an internal shearing force and moment or also only axial forces( tension)