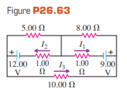
- #1
bob1352
- 6
- 1
- Homework Statement
- Just for practice, not for any assignment
- Relevant Equations
- Kirchhoff Voltage Rule, Sum of Voltage Drops in Loop is Equal to Zero.
I tried doing three loops. For the bottom I did 9-I1(1) + I2(1) - I3(10) -12 = 0, for the upper left corner I did 12 - I2(1)- I2(5) = 0, for the upper right corner I did 9 - I1(1) - I1(8) = 0. I came to I1 =1, I2 =2 and I3 = .2. This was incorrect, I don't think I am summing the currents correctly. I have attached an image of the problem.